“Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproduction” (“Akuserstvo, Ginekologia i Reprodukcia”) is a scientific and practical peer-reviewed journal for obstetricians, gynecologists and other experts in the area of women’s health. Our aims and priorities focus on scientific and information support to the members of the "professional community" in their pursuit of new ideas in obstetrics and gynecology research. In addition, the AGR journal proudly contributes to the continuing medical education (CME) of practitioners who specialize in various areas of women’s health including obstetrics, gynecology, in vitro fertilization (IVF) and assisted reproductive technology (ART).
“Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproduction” (“Akuserstvo, Ginekologia i Reprodukcia”) was founded in 2007
The impact factor of this journal, as shown in the Russian Science Citation Index (RSCI) is among the highest for the periodicals on obstetrics, gynecology, perinatology and problems of women’s health. According to RSCI, the biennial impact factor was 0.509 in 2013, 0.810 in 2014, and 0.976 in 2015.
The journal publishes original articles on clinical and experimental studies, as well as reviews on obstetrics, gynecology, and human reproduction. Special attention is paid to publications on CME as well as historic aspects of obstetrics and gynecology. All manuscripts, both original research and literature reviews, are published upon a mandatory peer-review.
Languages: Russian, English
Periodicity: 6 issues per year.
The printed versions are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License: full-text materials are freely available to the public in an open access repository.
Distribution of the printed version: Russia, the EurAsian Economic Community (EurAsEC) countries (Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Armenia, Moldova), Ukraine, Georgia.
The editorial board of “Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproduction” (“Akuserstvo, Ginekologia i Reprodukcia”) includes leading scientists from Russia, Austria, Great Britain, Israel, USA, Croatia, Ukraine, Georgia, and Uzbekistan.
The editorial board of this journal maintains the policy of full compliance with all principles of publishing ethics. Our ethical standards and codes conform to those of top international science publishers.
All submitted materials undergo a mandatory double-blind peer review.
Media Certificate of Registration: ПИ №FS77-34885 of December 29, 2008.
ISSN 2077-8333 (Print)
ISSN 2311-4088 (Online)
By the decision of the Higher Attestation Commission (HAC) of Russia, “Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproduction” (“Akuserstvo, Ginekologia i Reprodukcia”) is included in the "List of top peer-reviewed scientific journals and publications" where scientists seeking academic degrees are required to publish their results.
The “Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproduction” (“Akuserstvo, Ginekologia i Reprodukcia”) journal appears in the Russian Universal Scientific Electronic Library (RUNEB) elibrary.ru and is also present in the database of the Russian Science Citation Index (RSCI). Concise versions of major articles from this journal are published by the All-Russian Institute for Scientific and Technical Information (VINITI). The journal is also indexed by "Ulrich's periodicals Directory" – a global information system of periodicals and continued publications.
Current issue
ОRIGINAL ARTICLES 
What is already known about this subject?
► Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) in pregnant women is a common pathology on a global scale and has an adverse effect on pregnancy course and perinatal maternal and fetal outcomes.
► It is believed that intrauterine fetal pathology (chronic hypoxia, growth retardation, premature birth risk) is associated with placental insufficiency resulting from decreased blood oxygenation.
► The first-line therapy of IDA in pregnant women is based on oral medications. Drugs for intravenous administration are currently used insufficiently in pregnant women. More studies are required to assess their effect on pregnancy course and reduce risks of perinatal complications.
What are the new findings?
► It has been established that intravenously administered iron carboxymaltosate in pregnant women with moderate and severe IDA leads to effectively corrected anemia syndrome, contributes to prevention of fetal complications, lowers indications for blood transfusions and fewer postpartum infectious and inflammatory diseases.
► The best results in treatment of moderate and severe anemia in pregnant women with intravenous iron preparation are achieved when it is applied in the second trimester of pregnancy.
► IDA in pregnant women is accompanied by impaired blood rheological properties primarily increased small caliber-vessel blood viscosity, which may be one of the causes leading to placental insufficiency.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► It has been established that if oral therapy is ineffective, it is necessary to timely adjust therapeutic strategy and switch to using iron preparations for intravenous administration. For this, the optimal period is the second trimester of pregnancy because it saves a time window to prevent placental insufficiency.
► The data obtained allow to shape a new understanding of the pathogenesis behind placental insufficiency associated with impaired maternal blood rheological properties and declined blood flow in the utero-placental unit.
Aim: to assess perinatal maternal and fetal outcomes in women with iron deficiency anemia (IDA), based on the therapeutic approach and timing.
Materials and Methods. A non-interventional cohort study was conducted to assess the effectiveness of treatment with intravenously administered iron preparation in 65 pregnant women diagnosed with moderate-to-severe IDA: at 20–40 weeks of gestation 32 patients received treatment with intravenous iron (main group), 33 women received oral therapy (comparison group). Comparatively analyzed pregnancy course and outcomes based on the therapy protocol were assessed. At the gestational age of 20–23 and 35–40 weeks, clinical data, routine hemogram parameters (hemoglobin level, hematocrit, erythrocyte concentration, erythrocyte indices, total iron binding capacity), serum ferritin-related iron balance, blood viscosity indices within high and low shear rates were investigated.
Results. The groups turned out to be comparable in terms of the major indicators – age, parity, the time of anemia diagnosis, and the average hemoglobin level at the follow-up onset. In main group, after a course of intravenous administration of iron carboxymaltosate, the average hemoglobin level increased from 82.3 ± 6.1 g/L to 98.8 ± 6.8 g/L, for ferritin level – from 9.45 ± 0.28 µg/L to 28.35 ± 0.21 µg/L, total iron binding capacity decreased from 87.5 ± 1.72 mmol/L to 69.8 ± 1.03 mmol/L. In comparison group, the dynamics of indicators was markedly lower: the average hemoglobin level decreased from 87.5 ± 6.4 g/L to 84.5 ± 8.1 g/L, ferritin level decreased from 11.26 ± 0.12 µg/L to 9.47 ± 0.56 µg/L, whereas total iron binding capacity increased from 88.4 ± 0.18 µmol/L to 91.2 ± 1.2 µmol /L. Inter-group perinatal complications differed as well: in comparison vs. main group more often were observed untimely discharge of amniotic fluid (54.5 % vs. 28.1 %; p = 0.031), injuries to the soft tissues of the birth canal (28.1 % vs. 9.1 %; p = 0.048), obstetric bleeding (21.2% vs. 3.1%; p = 0.027), post-delivery infectious complications (24.2 % vs. 6.25 %; p = 0.045). Moreover, in comparison vs. main group there was a higher percentage of neonatal pathologies: fetal growth retardation (39.4 % vs. 15.6 %; p = 0.033), asphyxia at birth (45.5 % vs. 18.8 %; p = 0.015), hemorrhagic disorders (24.2 % vs. 6.3 %; p = 0.045). It was found that IDA was accompanied by deteriorated blood rheological properties manifested as increased viscosity at low shear rates (main group: at a rate of 3 s–1, the viscosity of whole blood was 6.63 ± 0.17 cPs, comparison group – 6.6 ± 0.13 cPs) in contrast to healthy pregnant women (5.54 ± 0.28 cPs) (p < 0.05). After intravenous iron therapy, blood viscosity at a shear rate of 3 s–1 decreased in main group to 5.68 ± 0.23 cPs and did not differ from control (p > 0.05). At the same time, blood viscosity in patients treated with oral drugs had no positive effect and remained at the level of 6.27 ± 0.12 cPs.
Conclusion. The use of intravenous iron carboxymaltosate in pregnant women in the second trimester is an effective approach to treat anemia that alleviates rate of perinatal complications and has a beneficial effect on blood rheological properties.
What is already known about this subject?
► The expansion of modern ideas about the multifactorial origin and heterogeneity of preeclampsia (РЕ) clinical manifestations has led to identifying new phenotypic variants of this pathology.
► Identification of early and late PE forms in pregnancy is of fundamental importance for assessing the prognosis and choosing tactics for patient’s management.
► The placental transcriptome plays an important role in regulating a crosstalk between the “static” genome and the “dynamic” proteome, making it a promising tool for studying РЕ underlying molecular mechanisms.
What are the new findings?
► The association between РЕ and defective trophoblast invasion, systemic inflammatory response, endothelial dysfunction, imbalanced angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors as well as metabolic disorders has been proven.
► MicroRNAs hsa-miR-656-3p, hsa-miR-151a-5p, hsa-miR-323a-5p, hsa-miR-4521, hsa-miR-519c-3p, hsa-let-7i-5p, hsa-miR-433-3p, hsa-miR-30d-5p, hsa-miR-548l, hsa-let-7g-5p, hsa-miR-214-5p, hsa-miR-27a-5p, hsa-miR-133b, hsa-miR-339-5p, hsa-miR-424-5p, hsa-miR-524-5p, hsa-miR-211-5p, hsa-miR-1283 were demonstrated to be involved in developing РЕ.
► A multidirectional expression of a set of placenta-specific microRNAs was proved in subgroups of pregnant women with early and late РЕ indicating existence of distinct pathophysiological vectors in developing analyzed obstetric pathology.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Changed expression for hsa-miR-656-3p, hsa-miR-151a-5p, hsa-miR-323a-5p, hsa-miR-4521, hsa-miR-519c-3p, hsa-let-7i-5p, hsa- miR-433-3p, hsa-miR-30d-5p, hsa-miR-548l, hsa-let-7g-5p, hsa-miR-214-5p, hsa-miR-27a-5p, hsa-miR-133b, hsa-miR-339-5p, hsa-miR-424-5p, hsa-miR-524-5p, hsa-miR-211-5p, hsa-miR-1283 allows to consider these microRNAs as potential biomarkers of developing early and/or late РЕ.
► The identified association between transcriptome changes and emerging obstetric pathology allows to update therapeutic approaches and strategies for patients with early and late РЕ.
Aim: to assess the molecular mechanisms in developing various clinical phenotypes of preeclampsia (PE) by analyzing specific placental tissue transcriptome patterns.
Materials and Methods. The prospective observational comparative study in parallel groups enrolled 43 pregnant women divided into 2 groups: main group – 23 pregnant women with diagnosed PE and control group – 20 apparently healthy women with uncomplicated pregnancy course, delivery and the postpartum period. To examine PE phenotypic features, the main group of pregnant women with PE was subsequently divided into 2 subgroups according to the date of pathology onset: early (n = 10) and late (n = 13) PE. Using the whole-genome next-generation sequencing (NGS), a comparative analysis of altered 18 microRNA level in placental tissue was carried out.
Results. Pregnant women with early PE compared to the control group were characterized by significantly low expression level for hsa-miR-656-3p (p < 0.001), hsa-miR-323a-5p (p = 0.017), hsa-miR-519c-3p (p = 0.019), hsa-let-7i-5p (p = 0.019), hsa-miR-433-3p (p = 0.019), hsa-let-7g-5p (p = 0.030), hsa-miR-214-5p (p = 0.030), hsa-miR-27a-5p (p = 0.031), hsa-miR-339-5p (p = 0.041), hsa-miR-524-5p (p = 0.045), hsa-miR-1283 (p = 0.049) and high expression for hsa-miR-151a-5p (p = 0.007), hsa-miR-4521 (p = 0.018), hsa-miR-30d-5p (p = 0.026), hsa-miR-548l (p = 0.027), hsa-miR-133b (p = 0.034), hsa-miR-424-5p (p = 0.042), hsa-miR-211-5p (p = 0.049). Patients with late PE had significantly decreased expression for hsa-miR-656-3p (p = 0.050) and
hsa-miR-574-3p (p = 0.017) as well as a significantly higher for hsa-miR-211-5p (p = 0.001) compared to the control group. Subgroup of women with early vs. late onset PE was characterized by significantly decreased expression level for hsa-miR-323-5p (p = 0.007) and overexpressed hsa-miR-30d-5p (p = 0.002), hsa-miR-5481 (p = 0.027).
Conclusion. The noted multidirectional expression for some microRNAs in subgroups of PE patients confirms the validity for stratification of such pathology based on two distinct phenotypic manifestations (early and late forms) and indicates the existence of different pathophysiological vectors in PE formation.
What is already known about this subject?
► Some infectious diseases serve as a trigger for developing autoimmune pathology, and autoantibodies, in turn, cause thrombosis development, aggravating disease severity.
► Considering the prominent similarity in immune mechanisms underlying thrombosis development between antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and COVID-19, some studies associate thrombogenesis trend in novel coronavirus infection with detected antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL).
► Within import substitution process generation of domestic tests for APS marker diagnostics was a pressing issue.
What are the new findings?
► A high aPL prevalence was noted in patients with verified COVID-19 in acute disease stage without previous APS history.
► Changes in the spectrum of aPL detection and circulation lasting for 9 months from the moment of diagnosis were also assessed for the first time.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The pathogenic aPL nature related to COVID-19 requires a detailed study contributing to delayed thrombogenesis in post-COVID period.
► Non-criteria vs. criteria aPL, such as anti-phosphatidylserine-prothrombin complex antibodies, may be more common justifying a need to include them into APS laboratory marker screening in COVID-19 patients.
► RPC Diagnostic Systems, Ltd. is the first domestic manufacturer of ELISA tests for APS markers detecting. The developed diagnostic kits successfully passed clinical trials and provide validated high analytical characteristics that may evidence about high reliability for the obtained test data in problematic field of laboratory diagnostics including autoimmune pathology.
Aim: to develop enzyme-linked immunosorbent tests for assessing the antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) markers and determine prevalence of three antiphospholipid antibody (aPL) types at different COVID-19 stages.
Materials and Methods. A comparative longitudinal controlled study was conducted by examining 120 subjects with COVID-19 diagnosis verified by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Donor serum samples collected before November 2019 were used as a control group. The laboratory study included measurement of IgA, IgM and IgG against β2-glycoprotein 1 (β2-GP1), cardiolipin, phosphatidylserine-prothrombin complex (PS-PT) by using domestically produced test systems based on indirect two-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
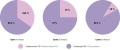
Results. Validation of the developed experimental tests was carried out in comparison with foreign commercial analogues in accordance with international standards. Alternative antigenic targets for effective diagnosis of antibodies against β2-GP1 were studied. Analyzing rate of aPL in patients at different COVID-19 stages showed that in acute vs. convalescence stage it was higher by 1.3-fold (81.7 and 65.0 %, respectively). The first rank detection place was assigned to IgG against β2-GP1, cardiolipin and PS-PT, the second – IgM against cardiolipin. The profile of the detected antibodies changed at various COVID-19 stages driven by time frame elapsed from the moment of diagnosis.
Conclusion. Recombinant constructs are created and analytical conditions are optimized for determining various aPL types. It was shown that along with other viral infections, COVID-19 triggers autoantibody production demonstrating that 54.2 % individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 were positive at least for one autoantibody type. The majority of such virus-associated aPL are presumably transiently positive.
What is already known about this subject?
► Compared with single pregnancy and spontaneous multiple pregnancy, multiple pregnancies resulting from applying assisted reproductive technologies (ART) are characterized by a large percentage of complicated course.
► An important arm in the pathogenesis of complicated pregnancy is presented by impaired gestational adaptation (GA) in the hemostasis system resulting from initial abnormalities and existing conditions for its altered functioning.
► Ovulation stimulation in ART can markedly affect gestational adaptation after in vitro fertilization.
What are the new findings?
► Hemostasis GA in multiple pregnancies undergoes profound changes revealed by level of fibrinogen, activated partial thromboplastin time, prothrombin time, thrombin time, anticoagulants and platelet aggregation activity.
► Rise in coagulation potential as early as in the first trimester is more prominent in induced pregnancy.
► GA in induced multiple pregnancies is at high risk of breach in compensatory mechanisms and requires monitoring for timely detection of decompensation signs and their correction.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The detection of early untimely gestational hyperadaptation in risk groups may allow to use methods for prevention of complicated gestational process after ART.
Aim: to assess adaptive hemostasis changes in multiple dichorionic pregnancy after in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Materials and Methods. A prospective observational randomized controlled trial was conducted by examining 58 and 46 pregnant women with multiple dichorionic diamniotic twins resulting from applying assisted reproductive technologies (ART) and spontaneous delivery (comparison group), respectively. Hemostasis parameters were studied as follows: activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), prothrombin time (PT), thrombin time (TT), fibrinogen, antithrombin, protein C, protein S, functions of protein С (РrоС Global test), D-dimer, platelet aggregation with adenosine-5-diphosphate (ADP), ristocetin, and collagen.
Results. A high coagulation potential was revealed, more prominent after using ART (p < 0.05). Fibrinogen level gradually increased while gestation age increased, whereas APTT, PT and TT level decreased. In the group with natural conception, fibrinogen increased by 22 % in the second trimester, reaching 4.5 g/L (95 % CI = 4,2–4,8) and by 6 % in the third trimester, reaching 4.8 g/L (95 % CI = 4,3–5,4), whereas in the IVF group – by 26 %, reaching 5.3 g/L (95 % CI = 4,7–5,6) and by 21 %, reaching (6.5 g/L; 95 % CI = 5,2–6,8) in relevant trimester of pregnancy, respectively. Antithrombin level was lower in IVF patients – 76.8 % (95 % CI = 72.6 – 81.0) in the second trimester, reaching 70.6 % (95 % CI = 64.8–76.4) in the third trimester (p < 0.001). Protein C level did not differ significantly between groups and was low within the reference range. The aggregatogram demonstrated a high platelet hemostatic potential in IVF patients (p < 0.05) as early as in the first trimester: ADP-induced aggregation – 68.3 % (95 % CI = 62.9–73.7), ristocetin-induced aggregation – 53.1 % (95 % = CI 48.7–58.5), collagen-induced aggregation – 58.4 % (95 % CI = 52.1–64.7). In the third trimester, both platelet aggregation and functional activity (ADP-induced aggregation – 64.5 % [95 % CI = 59.3–69.7], ristocetin-induced aggregation – 68.4 % [95 % CI = 63.2–73.6], collagen-induced aggregation – 50.7 % [95 % CI = 44.3–57.1]; p < 0.05) and D-dimer level persistently increased, also more prominently in the IVF group (1.60 ± 0.46 ng/ml; p < 0.05).
Conclusion. Gestational adaptation in induced multiple pregnancies is at high risk of breach in compensatory mechanisms and requires monitoring for timely detection of decompensation signs and their correction to prolong pregnancy till optimal delivery time frame.
What is already known about this subject?
► Preeclampsia (РЕ) is the leading cause of critical cases and maternal mortality in the worldwide.
► Predicting any pregnancy disease can minimize complications.
► There are algorithms for calculating РЕ risk, which, however, are associated with a large number of false negative results.
What are the new findings?
► An algorithm has been developed for calculating risk for patients in the border risk zone.
► The prediction approach presented here takes into account anamnestic data, first trimester screening as well as biochemical blood parameters.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The algorithm developed for predicting hypertensive disorders in pregnancy can be used in obstetrician-gynecologist practice for risk stratification of female patients in the border risk zone for timely administration of preventive measure and targeted therapy.
Introduction. In obstetrics, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) including preeclampsia (РЕ) are one of the primary causes resulting in critical cases and maternal mortality. HDP prediction is a milestone that allows preventing complications as well as reducing the number of most common relevant complications of pregnancy. Existing algorithms that predict PE risk distribute the risks in such a way that a considerable number of patients fall into the category of false negative results, and, consequently, receive no timely prevention and proper follow-up. In particular, this cohort usually consists of patients with borderline high risks, who may be designated as a medium risk group or located in a “gray” zone.
Aim: to develop a prognostic model for risk stratification in female patients with borderline to high developing PE risk based on combined first-trimester screening.
Materials and Methods. A prospective comparative study included 1089 female patients who underwent a combined screening at 11–14 weeks of gestation. Group 1 consisted of female patients at high РЕ risk (1:100 and greater), while female patients at moderate risk (1:101–1:250) and low risk (below 1:250) were included into Group 2 and Group 3, respectively. All pregnant women underwent examination including assessed anamnestic, general clinical and laboratory data, mean blood pressure (BP), uterine artery pulsatility index, serum level of human chorionic gonadotropin beta-subunits (β-hCG), placental growth factor (PlGF), pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A).
Results. An impact of various factors on risk of developing hypertensive disorders in pregnancy was assessed by binary logistic regression by identifying most significant among them and generating a statistical prediction model – the prognostic index of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy. The latter included: obstetric history, body mass index, PlGF, mean ВР, and alanine aminotransferase level. The sensitivity and specificity comprised 91.2 and 53.6 %, respectively, and the method effectiveness
was 81.8 %.
Conclusion. The method proposed for HDP prediction is a second-line approach that may be used in clinical practice to stratify patients with borderline high risk of developing PE.
What is already known about this subject?
► Lead is a widespread environmental pollutant holding the second place as most toxic metal after arsenic, which comprises 0.002 % of the Earth's crust.
► There is a large body of literature assessing lead exposure during pregnancy highlighted by variable presentations in newborns.
► Women of childbearing age chronically exposed to lead occupationally or environmentally have shown high rates of sterility, fetal and neonatal demise, with paired newborns suffering from growth retardation and diverse neurologic symptoms.
What are the new findings?
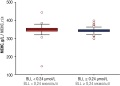
► A statistically significantly decreased mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) in babies born to mothers with blood lead level (ВLL) > 0.24 μmol/L vs. BLL < 0.24 μmol/L was detected that may evidence about lowered hemoglobin fetal production caused by lead intoxication.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Study corroborates an idea that pregnant women with occupational or environmental lead exposure should be monitored for BLL, which must be less 0.24 µmol/L during pregnancy.
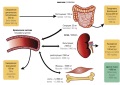
Introduction. More than 13 annual million deaths are caused by environmental pollutants worldwide. Urbanization, population growth, industrialization and globalization affect our lives both positively and negatively. Women can become lead exposed through occupational and environmental sources. Once lead enters the body, it is mainly deposited in diverse organs: brain, kidneys, liver and bones. The body stores lead mainly in the bones, where it accumulates over time that may be further released into the bloodstream during pregnancy, thus posing a threat to growing fetus.
Aim: to examine a lead impact on newborn hematological parameters during perinatal period.
Materials and Methods. A retrospective cohort study with 306 pregnant women and paired newborns was carried out. Peripheral blood lead level (BLL) in pregnant and postpartum women was analyzed by using the atomic-absorption spectrophotometry method. Blood specimens were collected for analysis in the third trimester of pregnancy. Newborns hemoglobin concentration (mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, MCHC) in erythrocytes was also assessed.
Results. We have detected a statistically significant decrease of MCHC in babies born to mothers with BLL > 0.24 µmol/L vs. BLL < 0.24 µmol/L. This difference may indicate a decline in hemoglobin fetal production caused by lead intoxication.
Conclusion. Study corroborates an idea that pregnant women with occupational or environmental lead exposure should be monitored for BLL, which should not exceed 0.24 µmol/L during pregnancy.
REVIEW ARTICLES 
What is already known about this subject?
► Magnesium plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism and insulin production, contraction of striated and smooth muscles, blood pressure control, maintained bone health, and exerts a tocolytic effect.
► Organic vs. inorganic magnesium salts have better bioavailability.
► Pyridoxine promotes better magnesium absorption and acts synergistically by playing a vital role in amino acid metabolism and neurotransmitter production.
What are the new findings?
► The high prevalence of magnesium deficiency has been demonstrated in recent large-scale studies in various human cohorts: pregnant women, women with hormone-dependent diseases and conditions, patients with malignant neoplasms of the reproductive system.
► Brand-name preparations containing organic magnesium salts in combination with pyridoxine in various forms should be used to compensate for magnesium deficiency allowing to ensure dosage accuracy, with the effectiveness and safety validated in clinical studies.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Combining pyridoxine with magnesium may provide additional advantages over either nutrient used alone.
► Magnesium deficiency replenishment should be an integral element in obstetric and gynecological care, promoting maternal and fetal well-being during pregnancy, improving outcomes in gynecological as well as gynecological oncological diseases.
Magnesium is an important cofactor for metabolic reactions involving more than 300 enzymes, regulating a series of fundamental processes, such as myocardial contraction and blood pressure control, glucose regulation, participation in neuromuscular transmission. The prevalence of magnesium deficiency in various cohorts of fertile age women comprises up to 73.8 %. In clinical studies it was demonstrated that magnesium deficiency is associated with diseases and states such as dysmenorrhea, premenstrual syndrome (PMS), polycystic ovary syndrome (POS), climacteric syndrome, osteoporosis, use of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and menopausal hormone therapy (MHT). Magnesium supplementation in combination with basic therapy can positively affect course and outcome of such pathologies. Magnesium organic salts could be used for countering magnesium deficiency. Among such agents, magnesium citrate has some advantage used in combination with pyridoxine (vitamin B6) providing additional effects. Health care professionals should be guided by the criteria for Mg-containing preparation selection, defined by the Russian Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (RSOG).
What is already known about this subject?
► Although conventional vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) treatment regimens are effective in relieving the disease symptoms, the data from long-term therapy are characterized by a high recurrence rate.
► The most common VVC causative agent is the polymorphic opportunistic fungus Candida albicans of the Cryptococcaceae family (76–89 %).
► The negative dynamics for VVС incidence last years reported in the studies is associated with rise in infection with Candida non-albicans strains resistant to most antifungal drugs.
What are the new findings?
► Preclinical studies of Ibrexafungerp (IBX) have demonstrated high antifungal activity against an extremely wide range of Candida isolates, including in vitro susceptibility to this drug observed in a number of echinocandin-resistant isolates such as C. albicans, C. parapsilosis, C. tropicalis, C. auris, C. krusei, C. glabrata, C. guilliermondii, C. lusitaniae, C. inconspicua. However, fungicidal activity against echinocandin-resistant FKS gene mutants (C. albicans, C. krusei, C. tropicalis, C. glabrata, C. auris) varied.
► Summarizing the results of phase II and III clinical trials, it can be argued that the IBX is effective against resistant fungal strains. The overall effectiveness in achieving clinical remission after IBX administration compared to standard treatment is 69.75 % versus 61 % for traditional methods of treatment.
► The percentage of patients with observed clinical recovery receiving IBX was 66.55 % that markedly exceeds that of in placebo group – 47.46 %.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► High IBX antifungal efficacy and a one-day dosage may further eliminate a need for unnecessarily long hospitalization and complex dosing schedules, thereby increasing adherence to therapy and odds for treatment success.
► The advantages related IBX such as extremely low toxicity, increased activity at low pH values accounting for high activity upon inflammation, long-term maintenance of a high drug concentration in body tissues during invasive diseases, low risk of undesirable drug interactions, allowing application of drug combinations and treatment of patients with multiple concomitant diseases, predict a marked success for this drug in clinical practice.
Introduction. Vulvovaginal candidiasis is an extremely common pathology of the female genital organs, leading to a long-term recurrent course and multiple complications. Although currently it is widely known about developing antibiotic resistance of bacterial pathogens, it is necessary to remember about similar phenomenon observed in other groups of infectious agents. In this regard, fungal infection also requires development of new therapeutic techniques and medicinal antifungal drugs, such as ibrexafungerp.
Aim: to analyze available publications revealing the mechanism of action, efficacy, antifungal spectrum and results of clinical trials for a new oral antifungal drug ibrexafungerp.
Materials and Methods. A search for publications in the electronic databases PubMed, eLibrary and ClinicalTrials.gov, published over the last 25 years was conducted using the following keywords in Russian and English: “candidiasis”, “vulvovaginal candidiasis”, “antifungal drugs”, “ibrexafungerp”, “clinical trials”, “mechanism of action”. Articles were assessed according to PRISMA guidelines. The titles and abstracts of identified publications were independently reviewed to retrieve relevant full text studies. After the selection procedure, 46 articles were included in the review.
Results. This review provides information on the creation of the drug ibrexafungerp, its mechanism of action, the activity against a relatively wide range of pathogens, as well as the results from 13 ongoing and completed clinical trials in patients with fungal infection.
Conclusion. The analysis of ibrexafungerp-related clinical studies showed its good oral bioavailability, high antifungal efficacy, so that its one-day dosage may further eliminate a need for unnecessarily long hospitalization and complex dosing schedules, thereby increasing adherence to therapy and odds for treatment success.
What is already known about this subject?
► Preterm delivery (PD) is one of the leading causes of neonatal mortality and morbidity worldwide.
► A risk factor for PD is isthmic-cervical incompetence (ICI) – shortening of the cervical length or dilatation of the cervical canal, often proceeding asymptomatic.
What are the new findings?
► Prophylactic progesterone treatment can reduce PD incidence in high-risk groups by more than 30 % .
► Installation of obstetric pessary or cervical suture reduces PD risk by preventing infection and premature rupture of the fetal membranes able to result in microbial invasion of the intrauterine cavity.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Early ICI detection, prevention and treatment can reduce PD risk.
Preterm delivery (PD) is a global public health problem, being the leading cause of perinatal morbidity and mortality in many countries. Despite numerous studies on the etiology of this condition, PD incidence has been increasing annually, and about 15 million infants are born prematurely (before the week 37 of gestation) worldwide. One of the main risk factors for PD is isthmic-cervical incompetence (ICI), which leads to microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity, prolapse of the fetal bladder, premature discharge of amniotic fluid and PD. Currently, several methods for ICI prevention and treatment are available: conservative (use of progesterone, obstetric pessary) and surgical (transvaginal cerclage and transabdominal cerclage).
What is already known about this subject?
► Bariatric surgery (BS) is able to provide substantial and long-term body weight loss as well as improved course of concomitant metabolic diseases, which leads to better quality of life and lowered mortality rate caused by cardiovascular complications and cancer.
► BS can reverse obesity-associated infertility as well as increase the rate of spontaneous conception.
► BS is associated with a high incidence of fetal growth retardation and a small gestational age fetus.
What are the new findings?
► The most preferred contraception method for post-BS patients is long-acting reversible contraceptives such as an intrauterine device.
► To timely identify, prevent and eliminate potential nutritional deficiencies in post-BS women, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive assessment and nutrition monitoring before, during and after pregnancy.
► Post-BS women are potentially susceptible to serious surgical complications in the postpartum period such as internal hernia, intestinal intussusception, intestinal obstruction, intestinal inversion and perforation, which led to maternal mortality.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Careful in-pregnancy monitoring focused on monitoring fetal growth and weight gain can be useful for early therapeutic intervention and, consequently, improved pregnancy outcomes.
► As a screening for gestational diabetes mellitus in post-BS women, it is recommended to conduct a capillary blood test.
► Early detection of psychological problems as well as consultation with a psychiatristis imperative.
Introduction. Obesity is a worldwide problem at epidemic scale. Bariatric surgery (BS) is the most effective method to treat morbid obesity characterized by long-term and positive effects on concomitant diseases. However, the effect of BS on female reproductive health has not been sufficiently studied to date, which makes relevant to conduct further investigations in this field.
Aim: to summarize research data assessing BS effect on female reproductive health.
Materials and Methods. There was conducted a search for publications in the electronic databases PubMed, eLibrary and Google Scholar to identify the following keywords and their combinations in Russian and English: "bariatric surgery", "reproductive health", "sex hormones", "pregnancy", "menstrual cycle", "fetal", "neonatal". The evaluation of the articles was carried out in accordance with the PRISMA recommendations. Based on search data, 868 publications from PubMed, 83 publications from eLibrary and 74 publications from Google Scholar were retrieved. After the selection procedure, 79 articles were included in the review.
Results. To date, the data regarding the long-term BS effects on improved obesity-related endocrine disorders remain insufficient. It is better to recommend long-acting reversible contraceptives such as intrauterine device, to post-BS patients. Women with BS history should have a continuous comprehensive nutritional assessment as well as blood macronutrients and trace elements monitoring before, during and after pregnancy. Recognizing potential complications associated with BS in the anamnesis and timely seeking specialized medical aid or timely transfer of a patient to a specialized medical facility may improve pregnancy outcomes for a mother and paired newborn.
Conclusion. While making decision to perform BS, it is necessary to fully understand its impact on female reproductive health, assess patients' reproductive intentions and fulfill health education obligations. All patients of childbearing age who are candidates for BS should participate in a joint decision-making dialogue on BS-related risks and benefits for reproductive health, which should be supported by extensive multidisciplinary work involving obstetricians, gynecologists, endocrinologists, psychologists and representatives of other medical specialties. To date, the data regarding the BS-related effects on pregnant women are heterogeneous, which requires additional investigations in this field.
What is already known about this subject?
► No unambiguous answer to the question regarding the mechanism of twins formation is currently available.
► Today, G.W. Corner’s theory considered dominant over more than 50 years has been criticized.
What are the new findings?
► A historical background about insights into twins formation is provided in the paper.
► Recent main theories and relevant evidence have been outlined.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Understanding twins formation mechanism can help to decrease the rate of iatrogenic twins in in vitro fertilization cycles.
What events in pregnant woman underlie twins formation? What do zygosity, chorionicity and amnionicity depend on? It seems that the answer is very clear. As early as in 1955, the works by G.W. Corner were published, which served as the basis for proposing the traditional model of twins formation, still remains widely acknowledged. But whether is everything so obvious? In order to answer this question, it is necessary to go back to the roots and understand of how the overall idea about fertilization and formation of multiple pregnancies has evolved since the XVII century till the present time.
FROM HISTORY 
Here, we describe the historical aspects of Nestor Maksimovich Maksimovich-Ambodik life and scientific work, as well as describe his contribution to the formation and development of obstetrics and gynecology in the Russian Empire.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ISSN 2500-3194 (Online)